We are your glycomics service provider for the best glycan analysis and glycan profile
Since 2016, we have been dedicated to serving both industry and academic clients with a broad portfolio of analytical services.
Our team comprises professional analytical chemists with decades of experience in mass spectrometry and sample preparation, ensuring accurate and reliable results for every project.
We pride ourselves on delivering exceptional service, and our high degree of customer satisfaction has enabled us to maintain long-term relationships with clients since day one.
Whether you need glycan analysis for research, development, or quality control purposes, you can trust us to provide superior services tailored to your specific needs.
We offer custom glycan analysis services for a wide range of biological samples:
- Serum antibodies and/or full serum glycan profile – immunoglobulins
- Saliva, urinary glycoproteins
- Recombinant purified proteins
- Protein extracts
- Exosomes
- Plant proteins
- Animal tissue
- Cell lines and cell line membranes
We also offer custom method development for non-standard or unpurified samples.
Addressing your needs in glycan profiling
Released glycan profiling
- Compare profiles between samples
- Tentative structure assignment
- Relative quantification
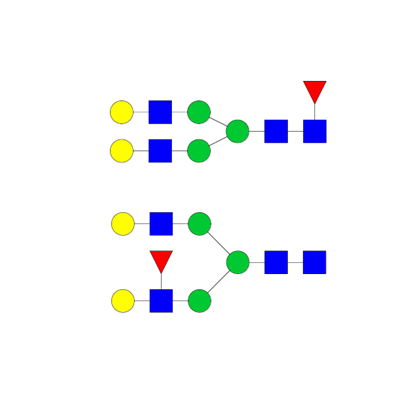
Structural elucidation
- Isomeric structures
- Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS)
- Synthetic standard
- Monosaccharide composition
- Sialic acid linkage (α 2,3 vs α 2,6)
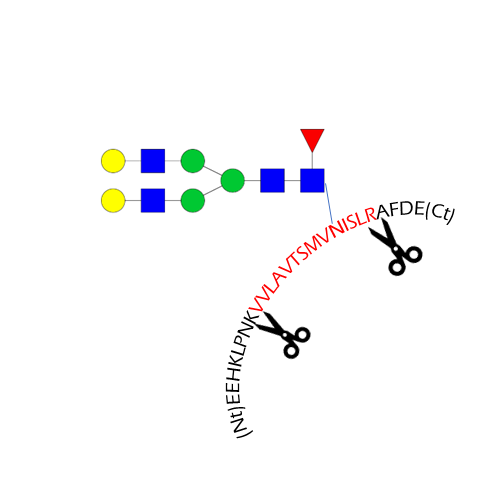
Glycosylation site analysis
- Glycosylation site occupancy
- Site-specific analysis of glycosylation
- Mutation N->X
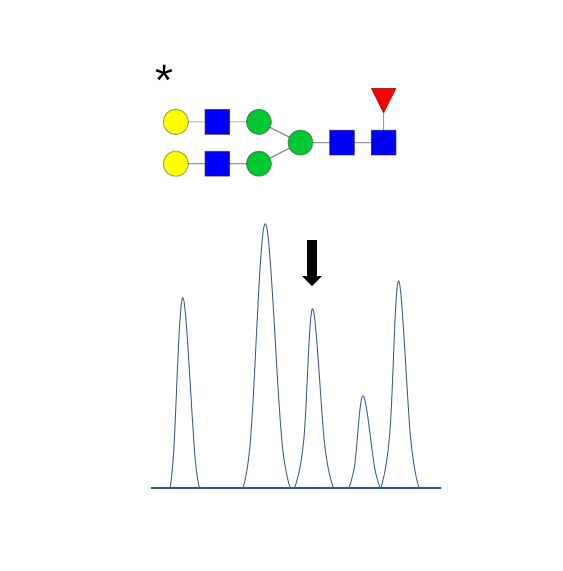
Absolute quantification
- Addition of stable isotope labeled (SIL) standards to the samples.
- CarboQuant
Glycan analysis can be very complex. We will help you choose the correct strategy to obtain the information you need. We offer a constantly updated portfolio of increasing complexity glycan analysis modules.
Applications:
Our analytical services have been used in biomarker discovery and validation studies, comparison of glycan profiles for different production cell lines, allergy research, process optimization, and early-stage biopharmaceutical development.
| Analysis type | Service | Method | Technique |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monosaccharide analysis | Monosaccharide composition and quantification | Extraction, reduction, or labeling with a fluorophore | LC-FLD-MS |
| Sialic acid analysis | Sialic acid quantification (NeuNac/NeuGc ratio) | Fluorescent labelling with DMB | LC-FLD |
| Oligosaccharides analysis | Milk oligosaccharide | Extraction, reduction, or labeling with a fluorophore | LC-FLD-MS |
| Released glycan profiling | N-glycan profiling | PGNase release, derivatization with a fluorophore | LC-FLD-MS |
| PGNase release, permethylation | MALDI-TOF | ||
| O-glycan profiling | chemical release, permethylation | MALDI-TOF or LC-MS | |
| Glycolipid profiling | Extraction and purification | LC-MS | |
| Structure elucidation | Sialic acid linkage type (α2,3 vs α2,6) | Stabilization of sialic acid residues by esterification/lactonization, derivatization with a fluorophore | MALDI-TOF or LC-FLD-MS |
| Glycan structure elucidation by MS/MS | Enzymatic or chemical release of glycans, derivatization | LC-MS/MS | |
| Digestion with exoglycosidases | Iterative exoglycosidase digestions, derivatization | LC-FLD-MS | |
| Glycosylation site analysis | Site occupancy | Protease digestion, glycan release with PNGase in 18O | LC-MS/MS |
| Site-specific analysis | Protease digestion, glycopeptide purification by HILIC | LC-MS/MS | |
| Mutation N->X | Protease digestion, purification, peptide analysis | LC-MS/MS | |
| Absolute quantification | Isotopic dilution, calibration curve | Addition of stable isotope labeled (SIL) standards to the samples | MALDI-TOF or LC-FLD-MS/(MS) |
Released glycan profiling
Analysis of released glycans by mass spectrometry and fluorimetry
To characterize the glycan population of purified glycoprotein or more complex samples.
N-glycans are enzymatically released from glycoproteins with glycosidase, for instance, PNGase whereas O-glycans are chemically released by reductive beta elimination.
Mass Spectrometry-based Glycomics Analytical Strategies
MALDI-TOF profiling of released glycans.
An efficient and economical way of profiling and comparing the major glycans between different samples. Glycans are permethylated to improve ionization efficiency and to stabilize sialic acid residues. It is possible to achieve absolute quantification by spiking the sample with our stable isotope labeled (SIL) glycan standards (CarboQuant).
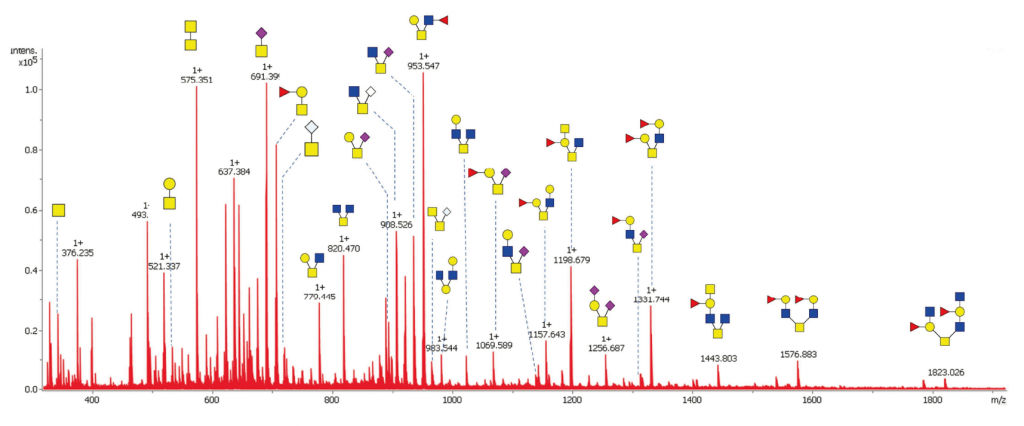
UHPLC-FLD-MS
Identification of the glycans present in a sample based on their mass and elution profile (retention time). Compared to a MALDI-TOF analysis, this method employs ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) with hydrophilic interactions (HILIC) for increased sensitivity and selectivity as it allows the separation of most isobaric isomers.
Glycans can be derivatized with a fluorophore like 2-AB, 2-AA, RapiFluor, or procainamide, which permits the relative quantification of all glycans in the mixture by fluorimetry. For the mass spectrometry analysis, we have access to the latest Q-TOF generation (SynaptXS, Waters) for accurate mass identification (5 ppm) and superior sensitivity.
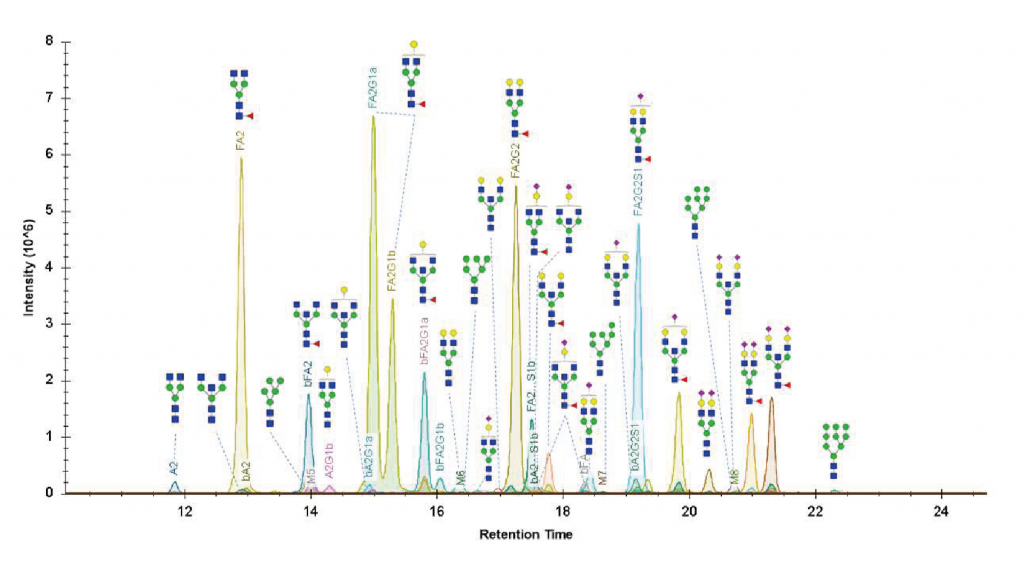
Glycan Structural Elucidation Service
The correct assignment of the structure of a glycan requires a more sophisticated analytical approach using tandem mass spectrometry. In addition, glycans’ fine structures can be investigated by successive exoglycosidase digestions or via chemical modifications of specific linkages.
Chemical derivatization of sialic acid linkage
This service is designed to differentiate the α-2,3 and α-2,6 sialic acid linkages by stabilization of the sialic acid residues by esterification/lactonization. The α2,6 sialic acid linkage is known to enhance anti-inflammatory activity and it reduces the toxicity of therapeutic antibodies. The type of sialic acid linkage also plays a role in viral tropism.
UHPLC-MS/MS
Collision-induced fragmentation of glycans in the gas phase is performed with a QqTOF mass spectrometer to generate fragment-ions and support the elucidation of a glycan structure.
Iterative digestion by exoglycosidases
Exoglycosidase enzymes can cleave glycans at specific linkage positions and monosaccharide residues. We can perform sequential digestions of a purified glycan with different exoglycosidases to assess the general structure, the monosaccharide type, and the stereochemistry of the glycosidic linkages (e.g. alpha or beta-linked galactose).
Use of reference standards
Ultimately, Glycan structures can be confirmed with a synthetic version that will display the same physicochemical properties (e.g. retention time, fragmentation pattern).
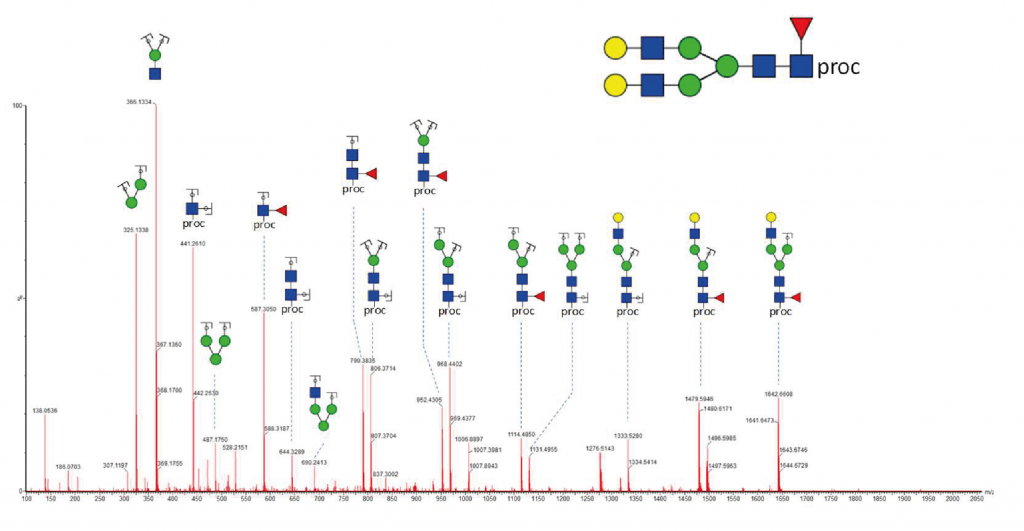
Glycosylation Site Mapping Service
Glycosylation site analysis provides information on the occupancy and glycans present on every potential glycosylation site. It requires the digestion of the glycoprotein by specific proteases (e.g., trypsin) to produce glycopeptides.
N-Glycosylation Site Occupation Analysis
This service provides the measurement of the occupancy or inoccupancy of a glycoprotein glycosylation site. When N-glycans are released by treatment with PNGase F, the asparagine is deamidated to aspartic acid and this mass change can be detected by MS. Additional heavy water labeling can be implemented to increase the mass shift of the deamidation to 3Da and to make the distinction between a glycosylated site and an artificial deamidation of an asparagine.
Site-specific analysis of glycosylation
This analysis intends to identify peptides with an attached glycan moiety in a single LC-MS/MS analysis. It is usually combined with a released glycan profiling and glycosylation site occupancy of the glycoprotein to improve confidence in the identification of the glycosylation sites and corresponding glycan structures
N to X mutations
Non-synonymous genetic mutations can lead to the substitution of an asparagine by another amino acid, and therefore eliminate N-glycosylation sites from the sequence of a protein. By specifically monitoring mutated peptides by LC-MS, it is possible to measure the presence of a mutated protein within the population.
Does the glycosylation occur at the right place and at the expected level?
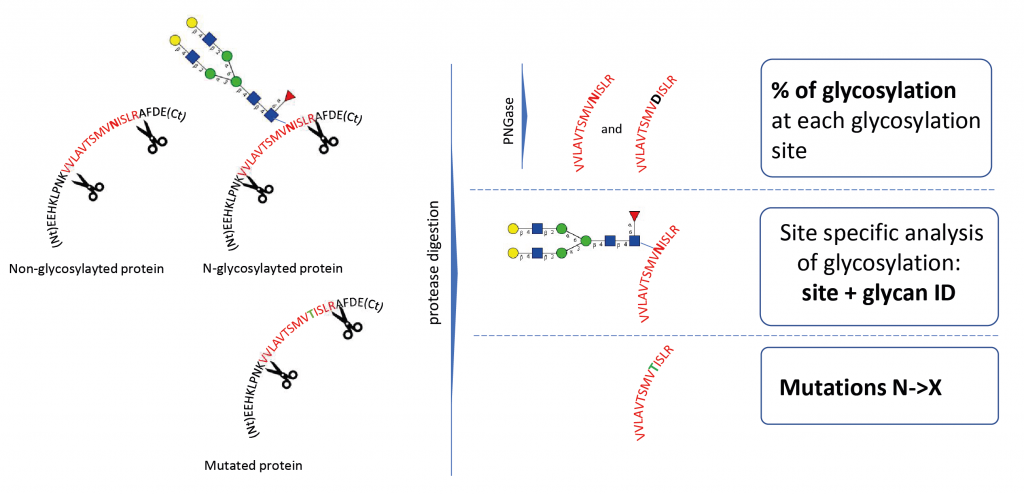
- Detection of under- or over-glycosylation at protein sequence level.
- Potential mutations that lead to the loss of glycosylation can be detected (e.g. N260Q in HIV)
Glycan Quantitation Services: Absolute quantification
Stable isotope labeling (SIL) consists of replacing specific atoms of a molecule with their stable heavier isotopes, typically 13C, 15N, and 18O. SIL molecules have an increased mass compared to their natural counterparts but similar chemical properties. The change in the mass can be detected by mass spectrometry and if the quantity of SIL in a sample is known, the quantity of the endogenous compounds can be inferred (isotopic dilution).
CarboQuant
Our CarboQuant HTS glycan quantification service is based on isotopic dilution and applied to the absolute quantification of N-glycans in IgG-type monoclonal antibodies by MALDI-TOF MS, both in low and high-throughput (up to 96 samples).
- Glycoanalysis of biologics
- Absolute quantification of biosimilar glycosylation
Synthesis of SIL-glycan standards
We can design and synthesize glycans or glycopeptides that have been quantified by quantitative NMR with stable isotope incorporation for any absolute quantification application.
Sialic Acid Analysis Service: Relative sialic acid quantification (NeuNAc/NeuGc ratio)
Quantitative analysis of sialic acids following Waters Corp. technical note “DMB-labeled Sialic acid analysis Using UPLC based BEH C18 columns”
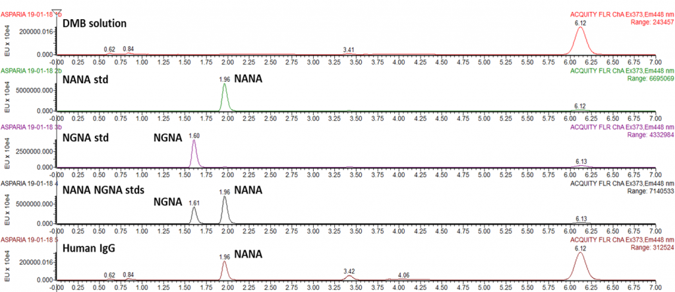
Workflow
- Mild acetic hydrolysis of sialic acid residues
- Fluorescent labeling with DMB
- Chromatographic separation of sialic acid derivatives by reverse phase UPLC and detection via fluorescence
- Peak assignment by comparison with external standards and mass spectrometry
Composition analysis of monosaccharides from lipids, proteins, free oligosaccharides (HMOs), or polysaccharides.
Analysis of free monosaccharides (e.g. cell culture media)
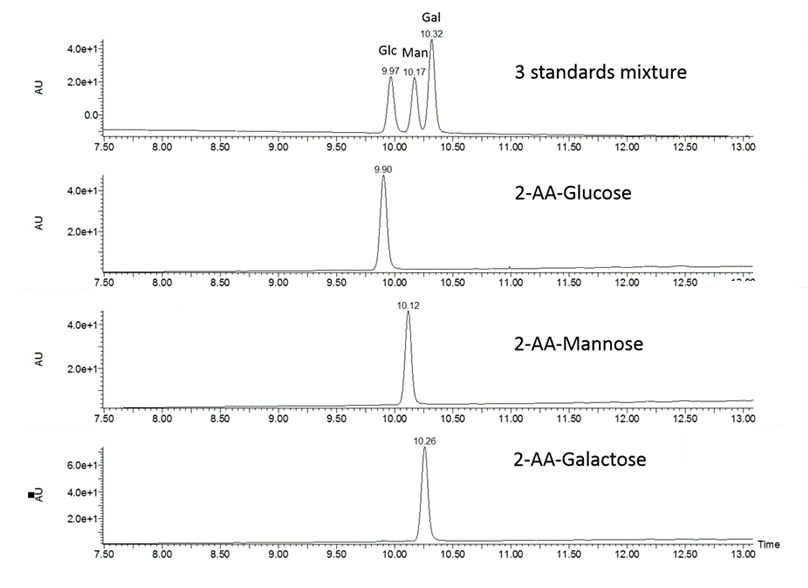
Workflow
- Acid hydrolysis of polysaccharides into monosaccharides
- Fluorescent labelling with 2-AA or 2-AB
- Liquid chromatography separation of labeled monosaccharides and detection by fluorescence
- Peak assignment by comparison with external standards and relative quantification
The instrumentation we use to analyze the glycan expression of your samples
Asparia Glycomics operates an analytical laboratory with state-of-the-art instrumentation for the preparation, purification, and characterization of glycan samples.
In addition, the company has access to high-end chromatography and mass spectrometry systems including a Bruker Ultraflex Extreme MALDI-TOF/TOF for rapid analysis of glycans using matrix-assisted desorption/ionization (MALDI).
Asparia Glycomics can also perform ultra-high-performance chromatography (UHPLC) separations of glycomics and glycoproteomics samples using hydrophobic (reversed phase) or hydrophilic interaction (HILIC) stationary phases.
The UHPLC systems are coupled with fluorimeter and high-resolution Q-TOF mass spectrometers. This includes the latest generation of Waters Synapt XS QTOF that provides increased sensitivity and allows for structure elucidation by MS/MS or ion mobility that separates molecules by their shape and charge state.

Waters Synapt XS
High-resolution accurate mass spectrometer with ion mobility analyzer for high sensitivity analysis and glycan’s structure elucidation.
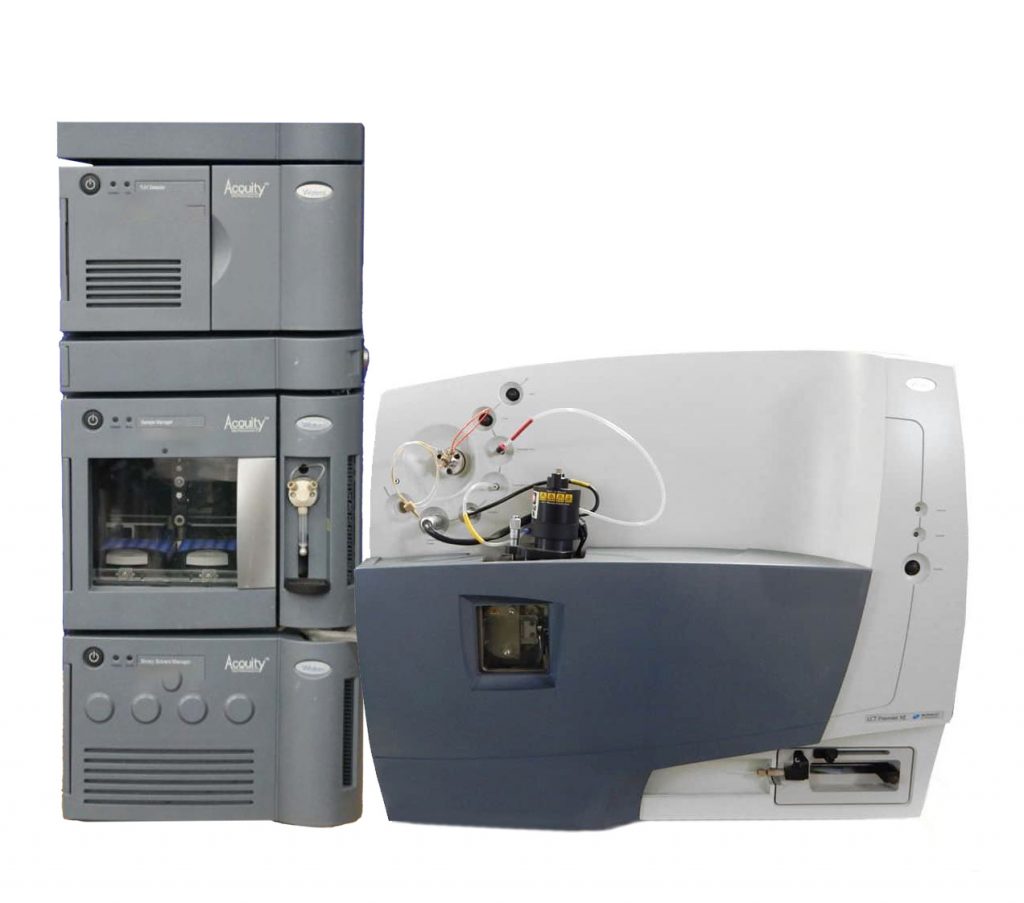

Waters Q-TOF LCT-Premier XE
Coupled with UPLC and FLD detection for glycoprofiling.
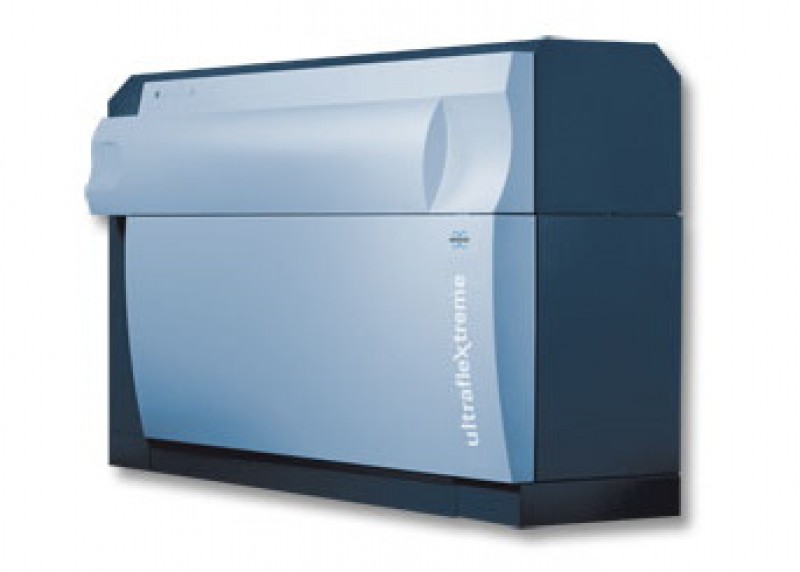

Bruker Ultraflex Extreme MALDI-TOF/TOF
Mass spectrometer for rapid analysis of glycans using matrix-assisted desorption/ionization (MALDI).

